The spelling neurone has become uncommon.
Skin nerve cell process.
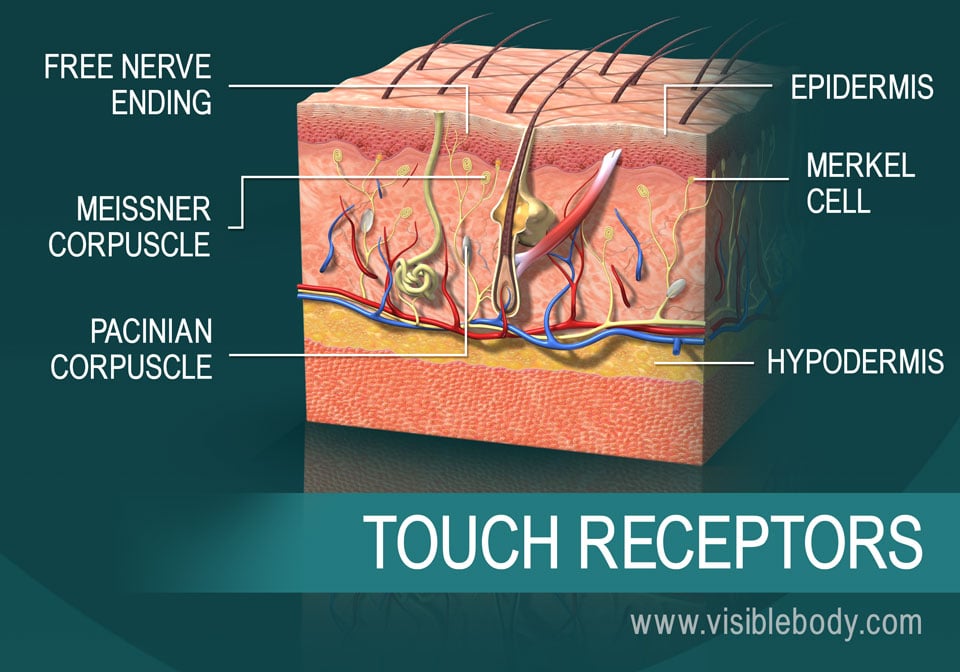
The dermis contains hair follicles sweat glands sebaceous oil glands blood vessels nerve endings and a variety of touch receptors.
These cells are very close to nerve endings in the skin.
An average square inch of skin contains 650 sweat glands 20 blood vessels and more than 1 000 nerve endings.
Basket cells these structures surround the base of hair follicles and serve as pressure sensors.
Skin is a complex organ.
A new method of generating mature nerve cells from skin cells could greatly enhance understanding of neurodegenerative diseases and could accelerate the development of new drugs and stem cell based regenerative medicine.
This moisture then evaporates and lowers the temperature of the skin.
Despite being just a few millimeters thick skin makes up.
The process slows down as you get older but it never stops.
Merkel cells are thought to be a type of skin neuroendocrine cell because they share some features with nerve cells and hormone making cells.
Neurons are typically classified into three types based on their function.
One average square inch 6 5 cm 2 of skin holds 650 sweat glands 20 blood vessels 60 000 melanocytes and more than 1 000 nerve endings.
The moisture serves as a cooling agent by making the surface of the skin moist.
Skin cells grow and divide in the basement membrane.
Skin cells die slough off and are replaced by new skin cells.
They are a source of valuable information when assessing overall nerve health and condition.
Merkel cells are found mainly at the base of the top layer of the skin the epidermis.
Cancer cells use nerve cell tricks to spread from one organ to the next by rockefeller university a mouse lung with metastases green formed by cancer cells that spread from a primary breast tumor.
A new method of generating mature nerve cells from skin cells could greatly enhance understanding of neurodegenerative diseases and could accelerate the development of new drugs and stem cell.
Plants and fungi do not have nerve cells.
Its primary function is to sustain and support the epidermis by diffusing nutrients to it and replacing the skin cells that are shed off the upper layer of the epidermis.